Lumbar Epidural Steroid Injection
Overview
Your spine has three sections. The lower back or spine is known as the lumbar section and supports your body weight and enables you to perform basic movements like getting up, walking, bending, and lifting. The other two sections are the cervical and thoracic.
Unfortunately, pressure on the lower back makes it more susceptible to developing painful injuries over time. Lumbar epidural steroid injections might relieve this discomfort.
Anatomy
The lumbar spine consists of bones known as vertebrae. This spinal region is where the spinal column ends and leads into a final collection of nerve roots (cauda equina).
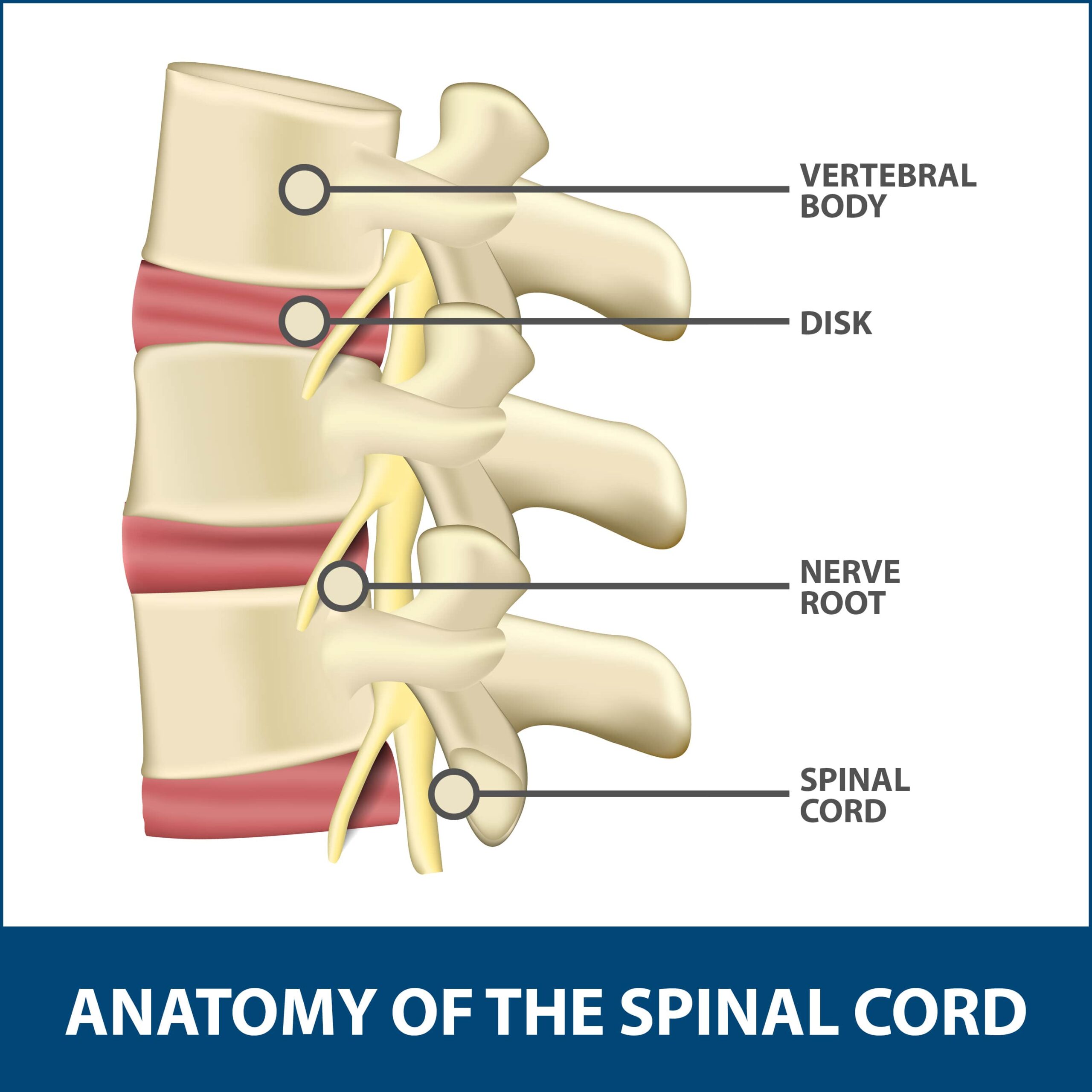
Description
When the lumbar bones and surrounding disks, muscles, nerves, or soft tissues undergo injury or exposure to illness, they can:
- Become damaged.
- Impact surrounding parts.
- Result in lower back pain.
- Cause bothersome and potentially life-influencing symptoms.
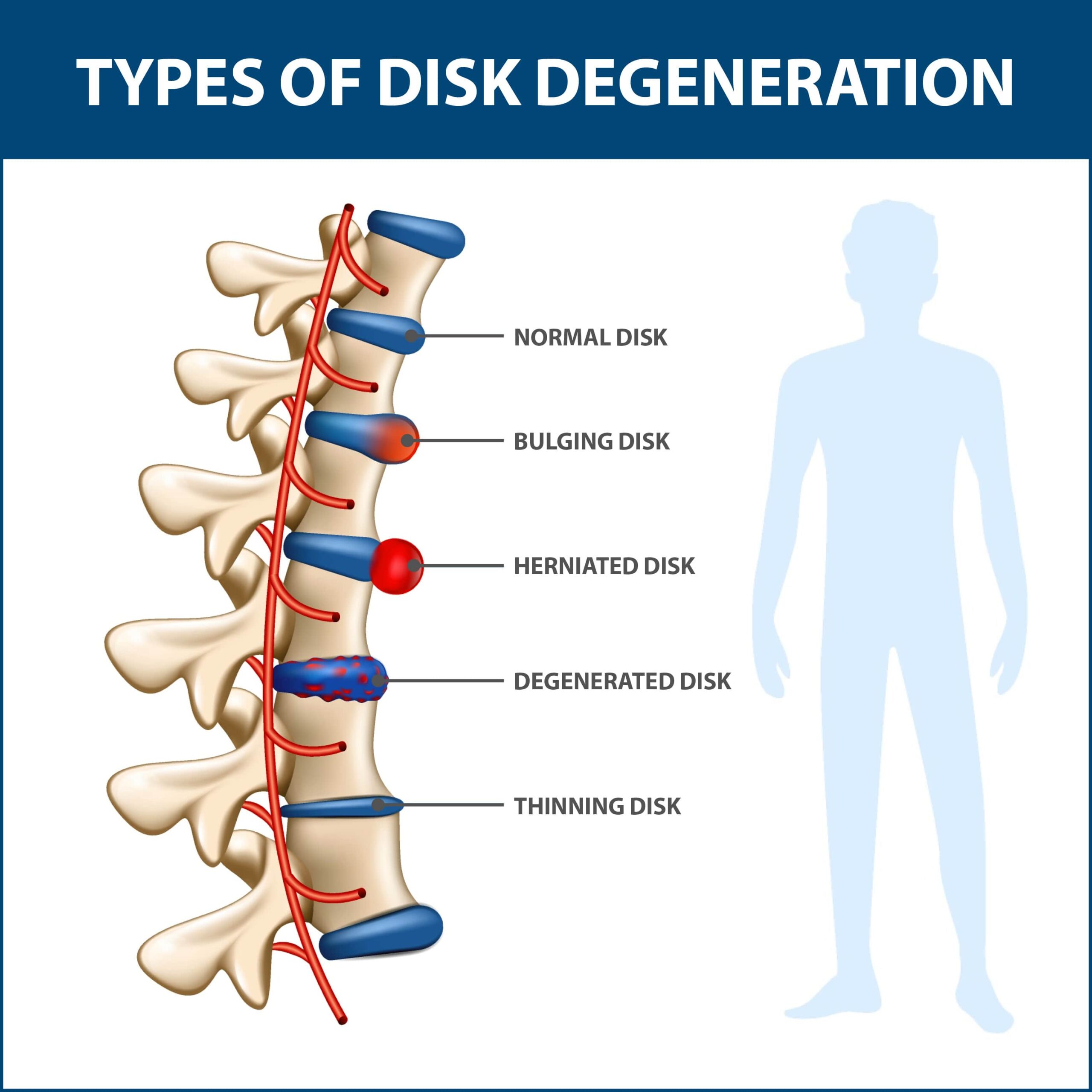
Common Causes of Lower Back Pain
Lower back pain often results from several conditions that relate to lumbar problems, including:
- Herniated Disks – Herniated disks occur when vertebrae-protecting disks develop an injury. Often this leads to pressure placed on neighboring nerves.
- Spinal Stenosis – Spinal stenosis results when open spaces in the spinal region narrow. As this space decreases, pressure is placed on nerves and other nearby components.
- Degenerative Disk Disease – As you age, lumbar disks gradually lose protective cushioning and flexibility. This natural degradation of disks results in a higher risk of damage or even complete breakage. Illnesses like osteoarthritis could also impact disk health.
- Sciatica – Lower back pain can come from damage or weakening of the sciatic nerve. The sciatic nerve travels down your lower back to your hips, buttocks, and legs.
- Risk Factors – Your chances of developing one of these conditions increases if you are:
- Middle-aged or older.
- Have a job requiring you to move awkwardly or place consistent and repetitive pressure on your lower back.
- A participant in a sport or leisure activity where physical contact or violent movements occur.
- Have to remain stationary for long periods of time.
You are also at higher risk if you have arthritis or other illness impacting your bones, muscles, and soft tissues.

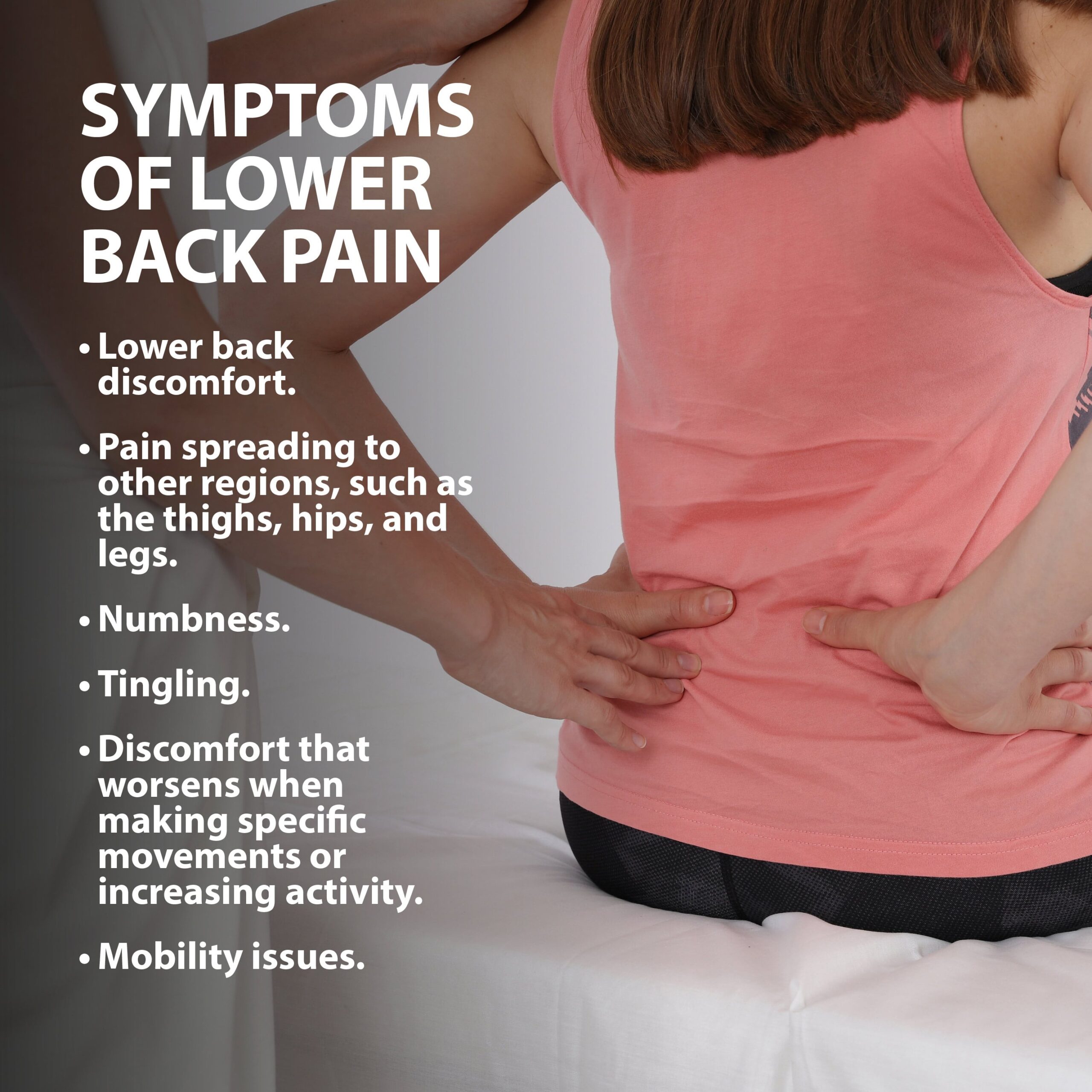
Symptoms
Besides lower back discomfort, lumbar spine-impacting injuries could lead to:
- Pain spreading to other regions, such as the thighs, hips, and legs.
- Numbness.
- Tingling.
- Discomfort that worsens when making specific movements or increasing activity.
In more severe instances, you might experience mobility issues.
Complications
If not properly identified and treated, you might develop potentially permanent issues like nerve damage.
Diagnosis
Your doctor will perform a physical exam and ask questions to understand your symptoms better. These may include:
- When did your pain begin?
- Where do you feel the discomfort most?
- Do any actions worsen your symptoms?
- Are you employed in a physically demanding job or participate in contact sports?
After asking these questions, your physician will check your lower back and look for noticeable abnormalities. Unfortunately, most conditions impacting the lumbar region require an X-ray or MRI.
Lumbar Epidural Steroid Injection
During this procedure, doctors administer steroids into the space surrounding your spine and surrounding nerves, known as the epidural region.
The Procedure
Lumbar epidural steroid injections can be performed using one of three major approaches:
- Caudal Route – Surgeons administer the injection into your lower back through the lower part of your epidural space. This is the most direct and simplest method of application.
- Transformational Route – Doctors inject steroids close to irritated nerves. This technique is considered to be the most precise.
- Interlaminar Route – Steroids are injected into the back of your spinal region. This method enables the medication to flow freely into the intended epidural spaces.

Intended Benefits
Following the procedure, most patients experience benefits like:
- Pain reduction.
- Decrease in inflammation.
- Improvement in mobility.
- Less reliance on over-the-counter or prescription medications.
The relief from these benefits can eliminate or delay the need for more aggressive treatment like surgery.
Preparation
Surgeons caution you not to consume any food or beverages for at least eight hours before your scheduled procedure time. The injection itself is usually done in an outpatient facility. You will likely be asked to prove that you are not driving yourself home and have an alternate method of transportation before being discharged.
It is important to disclose all medications you take in advance of the procedure. This is because certain drugs might increase your risk of complications.
What to Expect after Lumbar Epidural Steroid Injection
Following discharge, you are advised to return home, relax, and refrain from strenuous activities. Typically, you can return to work the next day if your job does not require heavy lifting.
If side effects occur, they are usually mild. The most common is slight soreness or discomfort at the injection site. You might find relief by using ice packs.
Outlook
You may notice pain reduction in as little as an hour or two following the shot. Pain relief is usually felt anywhere from three to five days post-injection.
Lasting pain reduction happens in approximately half of injection patients. Other factors might affect the process’s effectiveness, such as health, weight, physical fitness level, the condition causing your lower back pain, and the severity of the issue.
Injections can be re-administered on future occasions.
Next Steps
Talk with your Florida Orthopaedic Institute physician today to learn more about lumbar epidural steroid injection.
Areas of Focus
- Spine
- Anterior Cervical Corpectomy & Discectomy
- Artificial Disk Replacement (ADR)
- Bone Cement Injection
- Degenerative Disk Disease
- Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH)
- Discectomy
- Discitis Treatment & Information
- Epidural Injections for Spinal Pain
- Foraminotomy
- Interlaminar Implants
- Interlaminar Lumbar Instrumental Fusion: ILIF
- Kyphoplasty (Balloon Vertebroplasty)
- Kyphosis
- Laminectomy: Decompression Surgery
- Lumbar Epidural Steroid Injection
- Lumbar Interbody Fusion (IBF)
- Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery
- Outpatient Spine Surgery
- Pinched Nerve
- Piriformis Syndrome
- Sacroiliac Joint Pain
- Sciatica
- Scoliosis
- Spinal Fusion
- Spondylolisthesis and Spondylolysis
- Vertebroplasty
- Whiplash and Whiplash Associated Disorder (WAD)
The following Florida Orthopaedic Institute physicians specialize in Lumbar Epidural Steroid Injection:
Specialties
- AC Joint Injuries
- Achilles Tendinitis - Achilles Insertional Calcific Tendinopathy (ACIT)
- Achilles Tendon Rupture
- Achilles Tendonitis
- ACL Injuries
- Ankle Fracture Surgery
- Ankle Fractures (Broken Ankle)
- Ankle Fusion Surgery
- Anterior Cervical Corpectomy & Discectomy
- Arthroscopic Articular Cartilage Repair
- Arthroscopic Chondroplasty
- Arthroscopic Debridement of the Elbow
- Arthroscopy Of the Ankle
- Articular Cartilage Restoration
- Artificial Disk Replacement (ADR)
- Aspiration of the Olecranon Bursa - Fluid In Elbow
- Atraumatic Shoulder Instability
- Avascular Necrosis (Osteonecrosis)
- Bankart Repair
- Basal Joint Surgery
- Bicep Tendon Tear
- Bicep Tenodesis
- Bone Cement Injection
- Bone Growth Stimulation
- Bone Health Clinic
- Broken Collarbone
- Bunions
- Bursitis of the Shoulder (Subacromial Bursitis)
- Calcific Tendinitis of the Shoulder
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
- Charcot Joint
- Chiropractic
- Clavicle Fractures
- Colles’ Fractures (Broken Wrist)
- Common Foot Fractures in Athletes
- Community Outreach
- Cubital Tunnel Syndrome
- De Quervain's Tenosynovitis
- Deep Thigh Bruising
- Degenerative Disk Disease
- Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH)
- Discectomy
- Discitis Treatment & Information
- Dislocated Shoulder
- Dupuytren’s Disease
- Elbow
- Elbow Bursitis
- Elbow Injuries & Inner Elbow Pain in Throwing Athletes
- Epidural Injections for Spinal Pain
- Finger Dislocation
- Flexor Tendonitis
- Foot Stress Fractures
- Foot, Ankle & Lower Leg
- Foraminotomy
- Fractured Fingers
- Fractures Of The Shoulder Blade (Scapula)
- Fractures Of The Tibial Spine
- Functional Nerve Transfers of The Hand
- Ganglion Cysts
- General Orthopedics
- Glenoid Labrum Tear
- Golfer's Elbow
- Groin Strains and Pulls
- Growth Plate Injuries Of The Elbow
- Hallux Rigidus Surgery - Cheilectomy
- Hammer Toe
- Hamstring Injuries
- Hand & Finger Replantation
- Hand & Wrist
- Hand Nerve Decompression
- Hand Skin Grafts
- Hand, Wrist, Elbow & Shoulder
- Heat Injury/Heat Prostration
- High Ankle Sprain (Syndesmosis Ligament Injury)
- Hip & Thigh
- Hip Arthroscopy
- Hip Dislocation
- Hip Flexor Strains
- Hip Fractures
- Hip Hemiarthroplasty
- Hip Impingement Labral Tears
- Hip Muscle Strains
- Hip Pointers and Trochanteric Bursitis
- Hyperextension Injury of the Elbow
- Iliopsoas Tenotomy
- Iliotibial Band Syndrome
- Impingement Syndrome of the Shoulder
- Interlaminar Implants
- Interlaminar Lumbar Instrumental Fusion: ILIF
- Interventional Pain Management
- Interventional Spine
- Intraarticular Calcaneal Fracture
- Joint Replacement
- Knee & Leg
- Kyphoplasty (Balloon Vertebroplasty)
- Kyphosis
- Labral Tears Of The Hip (Acetabular Labrum Tears)
- Laminectomy: Decompression Surgery
- Lateral Collateral Ligament (LCL) Injuries
- Lisfranc Injuries
- Little League Shoulder
- LITTLE LEAGUER'S ELBOW (MEDIAL APOPHYSITIS)
- Lumbar Epidural Steroid Injection
- Lumbar Interbody Fusion (IBF)
- MACI
- Mallet, Hammer & Claw Toes
- Medial Collateral Ligament Injuries
- Meniscus Tears
- Metatarsalgia
- Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery
- Morton’s Neuroma
- Muscle Spasms
- Muscle Strains of The Calf
- Nerve Pain
- Neuromas (Foot)
- Neurosurgery
- Olecranon Stress Fractures
- Orthopaedic Total Wellness
- Orthopaedic Trauma
- Orthopedic Physician Or A Podiatrist? Definition of a Podiatrist
- Osteoarthritis of the Hip
- Osteoporosis
- Outpatient Spine Surgery
- Partial Knee Replacement
- Patellar Fracture
- Pelvic Ring Fractures
- Peripheral Nerve Surgery (Hand) Revision
- Pinched Nerve
- Piriformis Syndrome
- Piriformis Syndrome
- Plantar Fasciitis
- Plastic Surgery
- Podiatry
- Primary Care Sports Medicine
- Quadriceps Tendon Tear
- Radial Tunnel Syndrome (Entrapment of the Radial Nerve)
- Revascularization of the Hand
- Reverse Total Shoulder Replacement
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) of the Shoulder
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Of The Hand
- Robotics
- Rotator Cuff Tears
- Runner's Knee
- Sacroiliac Joint Pain
- Sciatica
- Scoliosis
- Senior Strong
- Shin Splints
- Shoulder
- Shoulder Arthritis
- Shoulder Arthroscopy
- Shoulder Injury: Pain In The Overhead Athlete
- Shoulder Replacement
- Shoulder Separations
- Shoulder Socket Fracture (Glenoid Fracture)
- SLAP Tears & Repairs
- Spinal Fusion
- Spine
- Spondylolisthesis and Spondylolysis
- Sports Foot Injuries
- Sports Hernias (Athletic Pubalgia)
- Sports Medicine
- Sports Wrist and Hand Injuries
- Sprained Ankle
- Sprained Wrist Symptoms and Treatment
- Subacromial Decompression
- Sudden (Acute) Finger, Hand & Wrist Injuries
- Targeted Muscle Reinnervation (TMR)
- Tendon Transfers of The Hand
- Tennis Elbow Treatment
- Thigh Fractures
- Thigh Muscle Strains
- Thumb Ulnar Collateral Ligament Injuries
- Total Ankle Replacement
- Total Hip Arthroplasty
- Total Hip Replacement - Anterior Approach
- Total Knee Replacement Surgery
- Trapezius Strain (Muscle Strain of The Upper Back)
- Traumatic Shoulder Instability
- Tricep Pain & Tendonitis
- Trigger Finger
- Turf Toe
- UCL (Ulnar Collateral Ligament) Injuries
- Ulnar Neuritis
- Valgus Extension Overload
- Vertebroplasty
- WALANT (Wide Awake Local Anesthesia No Tourniquet)
- Whiplash and Whiplash Associated Disorder (WAD)
- Wound Care
- Wrist Arthroscopy
- Wrist Fractures
- Wrist Tendonitis
Services
- Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation
- Physical Therapy
- Primary Care Sports Medicine
- PROMs (Patient-Reported Outcome Measures)
- Same-Day Orthopaedic Appointments Now Available
- Sports Medicine
- Sports-Related Concussion Treatment
- Telehealth Page
- Telemedicine
- Workers' Compensation
- Workers' Compensation Dispensary
- X-Ray
