Rheumatoid arthritis in the shoulder
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) of the shoulder is an autoimmune disease that results in your body essentially attacking healthy cells – specifically the ones found in the joints – as if they are a disease or intruder in the body. This causes the destruction of the tissue and cartilage in the shoulder, resulting in the bones rubbing together. This disease causes pain and swelling that worsens over time. Unfortunately, there is no known cure for RA of the shoulder. But there are many treatment options available to help you manage your pain and stay active.
Anatomy
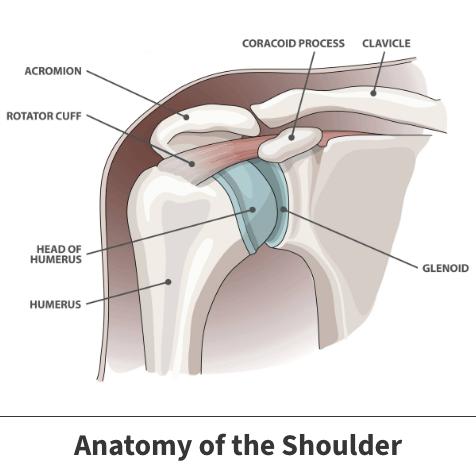
Your shoulder is made up of three bones: the upper arm bone (humerus), the collarbone (clavicle), and the shoulder blade (scapula). The head of your upper arm bone fits into a round socket (glenoid) in your shoulder blade. A combination of muscles and tendons (known as the rotator cuff) keeps your arm bone in the center of your shoulder socket.
The joints in your body have a lining covering them (synovium) that lubricates the joints, making it easier to move.
About
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease that causes your immune system to attack your own tissues – more specifically the shoulder tissue and joints. In RA, the defenses that protect the body from infection damage healthy tissue (such as cartilage and ligaments) instead. This causes the bones of the shoulder joint to rub together. This friction causes pain and potentially even bone spurs. Typically, it will affect both shoulders at the same time. When this particular type of arthritis affects the shoulder, it causes the lining of the joint to swell, also resulting in pain and stiffness.
There are two joints in the shoulder, both of which may be affected by arthritis.
- Acromioclavicular (AC) joint – The joint is where the collarbone meets the tip of the shoulder blade
- Glenohumeral joint – Where the head of the upper arm bone fits into the shoulder blade
To provide you with effective treatment, your physician will determine the joint experiencing pain and what type of arthritis you have.
The cause of rheumatoid arthritis is not fully understood. Genetics and environmental factors may both play a role. Unfortunately, there is no known cure for RA of the shoulder. But there are many treatment options available to help you manage your pain and stay active.
Symptoms
The main symptom of Rheumatoid Arthritis of the shoulder is pain that is brought on by any activity which progressively worsens. The other symptom of RA is a decrease in the range of motion. Over time, it may become increasingly difficult to lift your arm. You may hear a grinding, clicking, or snapping sound (known as crepitus) as you move your shoulder.
As the disease progresses, any movement of the shoulder causes pain. Night pain is common and sleeping can be difficult. Redness and warmth in the shoulder area are also common symptoms of RA of the shoulder.
Diagnosis
Your Florida Orthopaedic Institute physician will take a look at your symptoms, medical history, and overall health. After that, a physical examination. During this examination, your physician will look for:
- Signs of a previous injury
- Weakness (atrophy) in the muscles
- Pain when pressure is put on the joint
- Involvement of other joints
- A grating sensation inside the joint when moving
- Tenderness to touch
- Range of motion
- Any signs of injury to the muscle’s tendons and ligaments surrounding the joint
Your physician may also order X-rays to help better determine your diagnosis. X-rays are imaging tests that create in-depth pictures of dense structures, such as bone. If you have RA of the shoulder, this test will show a narrowing of the joint space, changes in the bone, and the formation of bone spurs (osteophytes).
Another tactic your physician may use to determine your diagnosis is to inject a local anesthetic into the joint. If it temporarily relieves the pain, then the diagnosis of RA is supported.

Treatment
There are both surgical and nonsurgical treatments available to help improve your symptoms and prevent your Rheumatoid Arthritis from worsening. Physicians recommend nonsurgical treatments first as they are the least invasive and tend to have good results. If non-surgical treatments are ineffective, then surgical procedures may be necessary.
Nonsurgical treatments
The initial treatment plan for Rheumatoid Arthritis of the shoulder is non-surgical. Your Florida Orthopaedic Institute physician may select any of the following to help relieve the symptoms of your RA:
- Rest
- Physical therapy to improve range of motion and strength
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs) such as aspirin, Advil/Motrin (ibuprofen) or Aleve (naproxen) to help reduce pain and swelling
- Corticosteroid injections in the shoulder to reduce pain and swelling
- Moist heat
- Icing your shoulder to reduce inflammation and pain
- Disease-modifying drugs, such as methotrexate, to help prevent the worsening of your RA
- Biologic treatments (disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs [DMARDs] – made with biotechnology) such as Actemra, Cimzia, Enbrel, Humira, Kineret, Orencia, Remicade, Rituxan, and Simponi. They are genetically engineered to act like natural proteins in your immune system
- Dietary supplements, such as glucosamine and chondroitin sulfate to help relieve pain
Surgical treatments
Your physician may consider surgery if none of the non-surgical treatments above relieve your symptoms. The surgical treatments used to treat RA of the shoulder include:
- Tendon repair – Inflammation and joint damage may cause tendons around your joint to loosen or rupture. In this procedure, the tendons around your shoulder joint are repaired.
- Joint fusion – Surgically fusing a joint may be necessary to stabilize or realign a joint and for pain relief when a joint replacement isn’t an option.
- Total joint replacement – During joint replacement surgery, your surgeon removes the damaged parts of your joint and inserts a prosthesis made of metal and plastic.
Lastly, the procedure chosen is highly dependent on the severity of your RA of the shoulder.
Videos
Related specialties
- AC Joint Injuries
- Atraumatic Shoulder Instability
- Bankart Repair
- Bicep Tenodesis
- Broken Collarbone
- Bursitis of the Shoulder (Subacromial Bursitis)
- Calcific Tendinitis of the Shoulder
- Clavicle Fractures
- Dislocated Shoulder
- Fractures of the Shoulder Blade (Scapula)
- Glenoid Labrum Tear
- Impingement Syndrome of the Shoulder
- Little League Shoulder
- Reverse Total Shoulder Replacement
- Rotator Cuff Tears
- Shoulder Arthritis
- Shoulder Arthroscopy
- Shoulder Injury: Pain in the Overhead Athlete
- Shoulder Replacement
- Shoulder Separations
- Shoulder Socket Fracture (Glenoid Fracture)
- SLAP Tears & Repairs
- Subacromial Decompression
- Trapezius Strain (Muscle Strain Of The Upper Back)
- Traumatic Shoulder Instability
