Functional nerve transfers of the hand
Nerves in the hand
Your hands have many important features, such as blood vessels, bones, soft tissues, and muscles. But without your nerves in the hand, you would experience difficulties or possibly even lose the ability to perform common, everyday activities, like lifting, gripping, or grasping objects.
Damage to the hand’s nerves can result in potentially serious disability. But in some cases, such an event can be treated through a medical procedure known as functional nerve transfers.
Anatomy
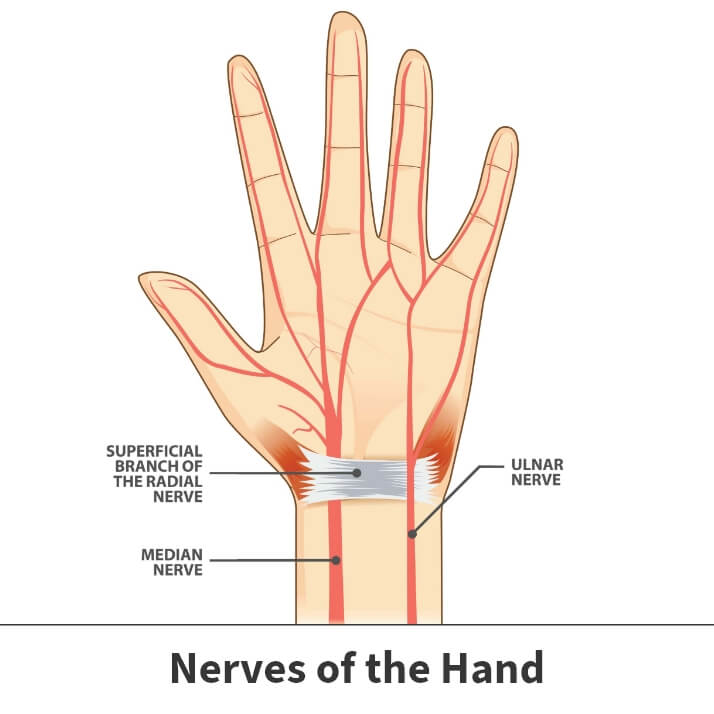
The hand has three primary nerves; the ulnar, radial, and median. These nerves carry messages to and from the body’s central nervous system, which instruct the hand’s muscles and bony structures like the fingers to move in different directions. Nerves also let you feel important sensations, including pain, warmth, and coldness. Badly damaged or diseased nerves lose the ability to carry these messages, which can result in serious mobility issues, possibly even paralysis of the affected area.
About
Fortunately, if you have suffered significant nerve damage resulting in potentially life-altering issues, you may be a candidate for functional nerve transfers. During this process, portions of one nerve are transferred to replace the injured or sickly section. The goal of this procedure is to restore as much of the nerve’s function as possible. Doing so can allow you to regain feeling, in addition to the ability to move and conduct basic activities.
Conditions that may increase the need for nerve transfer
Serious damage to the nerves can occur acutely – the result of some type of quick and unexpected event or chronically – over an extended period.
Acute nerve damage is often the result of some type of significant injury, such as an automobile accident, fall, or internal wound that pierces sensitive nerves. Chronic nerve injury can be caused by conditions like aging, years of overusing the hands or holding them in unusual positions, various nerve diseases, and nerve-hurting medical illnesses, including diabetes and immune system disorders.

Symptoms
Symptoms can vary depending upon the specific nerves involved, how bad the damage is, and the underlying problem causing the injury. But serious hand-related nerve damage can result in symptoms, including:
- Weakness
- Twitching or uncontrolled movements
- Pain around the affected nerve
- Numbness and tingling that spreads to other locations, such as the wrist or down the arm
- The inability to grip, grasp, or lift object
In the most severe cases, you may partially or completely lose the ability to move stricken hands.
Diagnosis
If your physician believes nerve damage might be the cause of your symptoms, they will ask about your health and professional history. If you have been diagnosed with illnesses like diabetes or an immune system problem, or have been employed in a profession where you perform a significant degree of computer work or heavy manual labor, your chances for developing chronic nerve damage increases.
Additional examination might include tests designed to measure your range, motion, and muscle tone. Other diagnostic tools they might use include:
- Blood tests to rule out diseases, like diabetes
- Bodily imaging scans like computerized tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. CT and MRI scans enable your doctor to examine your hand’s inner workings.
- Electromyography – these tests measure the electrical activity occurring inside muscles
Sometimes, your doctor may order a nerve biopsy. During this procedure, a small part of a nerve is removed from your body and examined for damage or abnormalities.
Treatment
If severe nerve damage is found, your physician will look out for several factors, which will help determine if you are a good candidate for nerve transfer. Considerations can include:
- Your age
- Your general health
- How bad your symptoms are
- The specific underlying problem and its severity
- How severe the damage is
- If other treatments might prove effective
Usually, nerve transfer is conducted on subjects with either severe nerve injury or significant disability.
The surgical process
The procedure begins with the surgeon making incisions over the sites of both the damaged and donor nerves. Then, the donor nerve is removed and inserted over the damaged nerve. Once this process is complete, the surgeon will stitch the nerves together.
Recovery
Typically, nerve transfers are performed on an outpatient basis, meaning you will not need a hospital stay. Following the procedure, you will likely need to undergo a course of physical therapy geared towards helping you regain movement.
Related specialties
- Basal Joint Surgery
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
- De Quervain's Tenosynovitis
- Dislocated Finger
- Distal Radius Fracture (Broken Wrist)
- Dupuytren’s Disease
- Flexor Tendonitis
- Fractured Fingers
- Ganglion Cysts
- Hand & Finger Replantation
- Hand Nerve Decompression
- Hand Skin Grafts
- Nerve Pain
- Peripheral Nerve Surgery (Hand) Revision
- Revascularization of the Hand
- Rheumatoid Arthritis of the Hand
- Sports Wrist & Hand Injuries
- Sprained Wrist
- Sudden Acute Finger, Hand & Wrist Injuries
- Targeted Muscle Reinnervation (TMR)
- Tendon Transfers of the Hand
- Thumb Ulnar Collateral Ligament Injuries
- Trigger Finger
- Ulnar Neuritis
- WALANT (Wide Awake Local Anesthesia No Tourniquet)
- Wrist Arthroscopy
- Wrist Fractures
- Wrist Tendonitis
